Diabetes Insipidus Neurogenic Vs Nephrogenic
Nephrogenic diabetes insipidus is a disorder of water balance. the body normally balances fluid intake diabetes insipidus neurogenic vs nephrogenic with the excretion of fluid in urine. however, people with nephrogenic diabetes insipidus produce too much urine (polyuria), which causes them to be excessively thirsty (polydipsia). More diabetes insipidus neurogenic vs nephrogenic images. What is the difference between nephrogenic and neurogenic diabetes insipidus? nephrogenic diabetes insipidus is from the word “nephro” meaning kidneys. this indicates that the cause of the increase in urine output is due to a problem in the kidney. in diabetes insipidus, more than 2. 5 liters of urine is excreted per day. There are two main types of di that affect cats: neurogenic (or central diabetes insipidus) and nephrogenic diabetes insipidus. in neurogenic di, the cause is due to a lack of the hormone vasopressin, which regulates the body's retention of water.
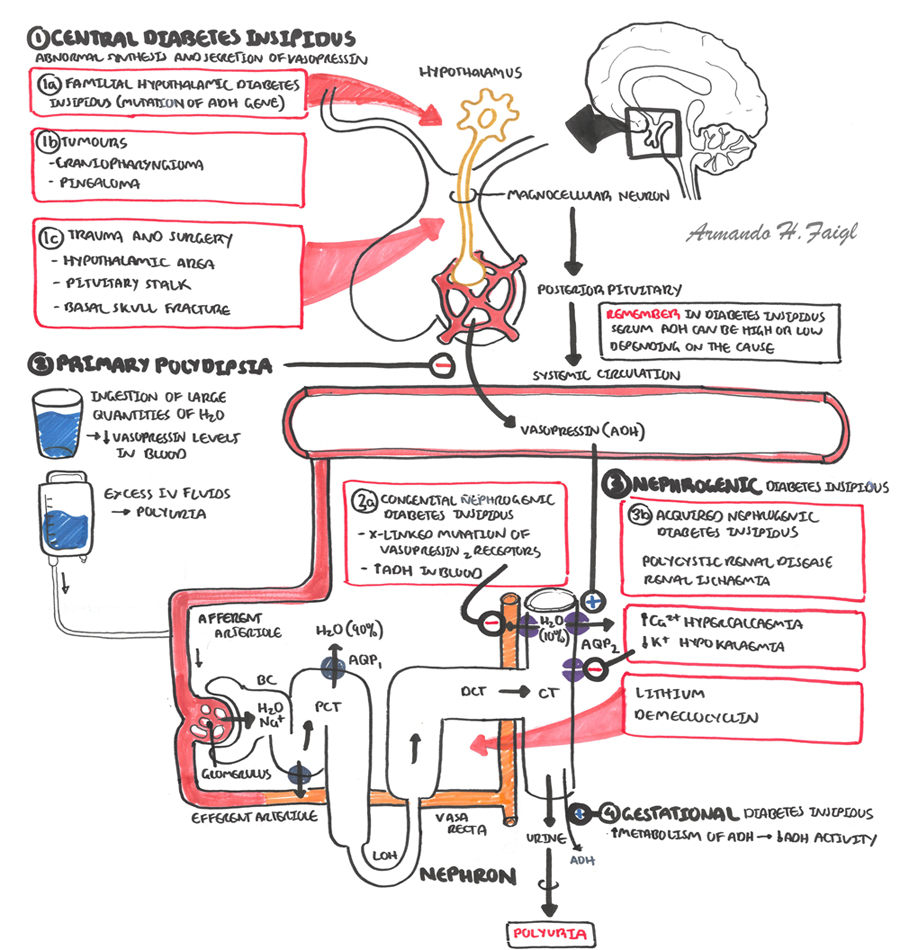
Central diabetes insipidus is completely unrelated to diabetes, even though they share the symptoms of peeing more and feeling thirsty. it's also called "central di," "pituitary di," "hypothalamic. Nephrogenicdiabetesinsipidus (ndi) is a form of diabetes insipidus primarily due to pathology of the kidney. this is in contrast to central or neurogenic diabetes insipidus, which is caused by insufficient levels of antidiuretic hormone (adh, also called vasopressin). nephrogenic diabetes insipidus is caused by an improper response of the diabetes insipidus neurogenic vs nephrogenic kidney to adh, leading to a decrease in the ability of. Nephrogenicdiabetesinsipidus. ndi results from the failure of the kidney to respond to avp. urine production in patients with ndi is typically 12 l/day. children usually present with the inherited form whereas adults present with the acquired form of ndi [table 2].
Nephrogenicdiabetesinsipidus (ndi) is a rare kidney disorder that may be inherited or acquired. ndi is not related to the more common diabetes mellitus (sugar diabetes), in which the body does not produce or properly use insulin. ndi is a distinct disorder caused by complete or partial resistance of the kidneys to arginine vasopressin (avp). Hereditary nephrogenic diabetes insipidus (ndi) is characterized by inability to concentrate the urine, which results in polyuria (excessive urine production) and polydipsia (excessive thirst). affected untreated infants usually have poor feeding and failure to thrive, and rapid onset of severe dehydration with illness, hot environment, or the withholding of water.
Nephrogenicdiabetesinsipidus Wikipedia
Diabetesinsipidus results from a deficiency of vasopressin (antidiuretic hormone [adh]) due to a hypothalamic-pituitary disorder (central diabetes insipidus) or from resistance of the kidneys to vasopressin (nephrogenic diabetes insipidus). polyuria and polydipsia develop. diagnosis is by water deprivation test showing failure to maximally concentrate urine; vasopressin levels and response to. Nephrogenic diabetes insipidus is a form of diabetes diabetes insipidus neurogenic vs nephrogenic insipidus primarily due to pathology of the kidney. this is in contrast to central or neurogenic diabetes insipidus, which is caused by insufficient levels of antidiuretic hormone. nephrogenic diabetes insipidus is caused by an improper response of the kidney to adh, leading to a decrease in the ability of the kidney to concentrate the urine by removing free water. Nephrogenicdiabetesinsipidus. in some cases, nephrogenicdiabetesinsipidus goes away after treatment of the cause. for example, switching medications or taking steps to balance the amount of calcium or potassium in the patient’s body may resolve the problem. medications for nephrogenic diabetes insipidus include diuretics, either alone or.
Schliefer k, rockstroh jk, spengler u, sauerbruch t. nephrogenic diabetes insipidus in a patient taking cidofovir. lancet 1997; 350:413. navarro jf, quereda c, quereda c, et al. nephrogenic diabetes insipidus and renal tubular acidosis secondary to foscarnet therapy. am j kidney dis 1996; 27:431. To distinguish between central and nephrogenic diabetes insipidus, first obtain a plasma avp level and then determine the response of the urine osmolality to a dose of avp (or preferably, the v2.
Nephrogenicdiabetesinsipidus is a long name for an uncommon condition. nephrogenic diabetes insipidus is not the same as diabetes mellitus. diabetes mellitus causes elevated blood sugar levels. Hereditary nephrogenic diabetes insipidus (ndi) is characterized by inability to concentrate the urine, which results in polyuria (excessive urine production) and polydipsia (excessive thirst). affected untreated infants usually have poor feeding and failure to thrive, and rapid onset of severe dehydration with illness, hot environment, or the withholding of water. short stature and secondary. Central diabetes insipidus. damage to the pituitary gland or hypothalamus from surgery, a tumor, a head injury or an illness can cause central diabetes insipidus by affecting the usual production, storage and release of adh. an inherited genetic disease can also cause this condition. nephrogenic diabetes insipidus. Diabetesinsipidus (di) is defined as the passage of large volumes (>3 l/24 hr) of dilute urine (< 300 mosm/kg). it has the following 2 major forms: central (neurogenic, pituitary, or neurohypophyseal) di, characterized by decreased secretion of antidiuretic hormone (adh; also referred to as arginine vasopressin [avp]) nephrogenic di, charac.
What is the difference between nephrogenic and neurogenic diabetes insipidus? nephrogenic diabetes insipidus is from the word “nephro” meaning kidneys. this indicates that the cause of the increase in urine output is due to a problem in the kidney. in diabetes insipidus, more than 2. 5 liters of urine is excreted per day. the excretion of…. Nephrogenicdiabetesinsipidus is a disorder of water balance. the body normally balances fluid intake with the excretion of fluid in urine. however, people with nephrogenic diabetes insipidus produce too much urine (polyuria), which causes diabetes insipidus neurogenic vs nephrogenic them to be excessively thirsty (polydipsia). affected individuals can quickly become dehydrated if they do not drink enough water, especially in hot. Nephrogenicdiabetesinsipidus (ndi) is a rare disorder that occurs when the kidneys are unable to concentrate urine. in most people, the body balances the fluids you drink with the amount of. Diabetes insipidus (di) is defined as the passage of large volumes (>3 l/24 hr) of dilute urine (< 300 mosm/kg). it has the following 2 major forms: central (neurogenic, pituitary, or neurohypophyseal) di, characterized by decreased secretion of antidiuretic hormone (adh; also referred to as arginine vasopressin [avp]) nephrogenic di, charac.
Nephrogenic diabetes insipidus (ndi): what is it?.
Diabetesinsipidus Niddk
Nephrogenicdiabetesinsipidus (ndi): what is it?.
Nephrogenic diabetes insipidus (ndi) is an inability to concentrate urine due to impaired renal tubule response to vasopressin (adh), which leads to excretion of large amounts of dilute urine. it can be inherited or occur secondary to conditions that impair renal concentrating ability. Diabetes insipidus (di) is a condition characterized by large amounts of dilute urine and increased thirst. the amount of urine produced can be nearly 20 liters per day. [1] reduction of fluid has little effect on the concentration of the urine. [1]. Nephrogenic diabetes insipidus (ndi) is a rare disorder that occurs when the kidneys are unable to concentrate urine. in most people, the body balances the fluids you drink with the amount of. Nephrogenicdiabetesinsipidus (ndi) is an inability to concentrate urine due to impaired renal tubule response to vasopressin (adh), which leads to excretion of large amounts of dilute urine. it can be inherited or occur secondary to conditions that impair renal concentrating ability.
Diabetesinsipidus (di) is a condition characterized by large amounts of dilute urine and increased thirst. the amount of urine produced can be nearly 20 liters per day. reduction of fluid has little effect on the concentration of the urine. complications may include dehydration or seizures.. there are four types of di, each with a different set of causes. Diabetesinsipidus and syndrome of inappropriate anti-diuretic hormone [siadh] have some similarities, but are two very different conditions. they both involve how the body create vasopressin [adh] and one of the primary symptoms of both conditions is excessive thirst, but the results are completely the opposite. in diabetes insipidus, the body is excreting too many Nephrogenic diabetes insipidus is not the same as diabetes mellitus. diabetes mellitus causes elevated blood sugar levels. but nephrogenic diabetes insipidus is due to a problem in the kidneys. in.
Comments
Post a Comment