Diabetes Melitus Normal

Continued type 2 diabetes. type 2 diabetes used to be called non-insulin-dependent or adult-onset diabetes. but it’s become more common in children and teens over the past 20 years, largely. Chronic diabetes conditions include type 1 diabetes and type 2 diabetes. potentially reversible diabetes conditions include prediabetes — when your blood sugar levels are higher than normal, but not high enough to be classified as diabetes — and gestational diabetes, which occurs during pregnancy but may resolve after the baby is delivered.
Diabetesmellitus an easy to understand guide covering causes, diagnosis, symptoms, treatment and prevention plus additional in depth medical information. a normal fasting blood sugar level is between 70 and 100 milligrams per deciliter (mg/dl). diabetes is diagnosed if the fasting blood sugar level is 126 mg/dl or higher. Diabetesmellitus is a disorder in which the amount of sugar in the blood is elevated. doctors often use the full name diabetes mellitus, rather than diabetes alone, to distinguish this disorder from diabetes insipidus. diabetes insipidus is a relatively rare disorder that does not affect blood glucose levels but, just like diabetes mellitus.
2019-05-27 overview for normal glucose digestion and diabetes mellitus. diabetes mellitus imagine your self tracking the fate of carbohydrates you eat starting with your digestive system, blood, then each cell in your body. Diabetesmellitus (dm), commonly known as diabetes, is a group of metabolic disorders characterized by a high blood sugar level over a prolonged period of time. symptoms often include frequent urination, increased thirst, and increased appetite. if left untreated, diabetes can cause many complications. acute complications can include diabetic ketoacidosis, hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state, or. The american diabetes mellitus association’s objectives for blood glucose control in people with diabetics issues are 70 to 130 mg/dl before meals, and also less than 180 mg/dl after meals. {normal blood sugar levels for diabetes type 2 chart.
Diabetesmellitus is a disease that prevents your body from properly using the energy from the food you eat. diabetes occurs in one of the following situations: blood glucose levels usually return to normal after childbirth. however, women who have diabetes melitus normal had gestational diabetes have an increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes later in life. Understanding blood glucose level ranges can be a key part of diabetes self-management. this page states ‘normal’ blood sugar ranges and blood sugar ranges for adults and children with type 1 diabetes, type 2 diabetes and blood sugar ranges to determine people with diabetes.. if a person with diabetes has a meter, test strips and is testing, it’s important to know what the blood glucose. With type 2 diabetes, your body doesn’t use insulin well and can’t keep blood sugar at normal levels. about 90-95% of people with diabetes have type 2. it develops over many years and is usually diagnosed in adults (but more and more in children, teens, and young adults). Diabetes is an inability of the body to regulate blood sugar often caused by an abnormality of the pancreas. it causes increased thirst, urination, appetite, and weight loss. most dogs have type 1 diabetes caused by total or near destruction of the insulin producing cells and so insulin injections are required for treatment. diabetes is diagnosed by detecting increased levels of glucose in the.
Diabetesmellitus Type 1 Type 2 And Gestational Diabetes
Maintain your blood cholesterol and triglyceride (lipid) levels as near the normal ranges as possible. control your blood pressure. your blood pressure should not go over 140/90. decrease or possibly prevent the development of diabetes-related health problems. you hold the keys to managing your diabetes by:. Maintain your blood cholesterol and triglyceride (lipid) levels as near the normal ranges as possible. control your blood pressure. your blood pressure should not go over 140/90. decrease or possibly prevent the development of diabetes-related health problems. you hold the keys to managing your diabetes by:. Diabetes mellitus—a disease defined by biomarkers. diabetes mellitus (dm) is a global epidemic that encompasses multiple disorders related to altered metabolic homeostasis of glucose and related systems. although diabetes can manifest as an autoimmune disease of pancreatic islet cells (the primary mechanism in type 1 diabetes), gestational.
Diabetesmellitus, also called diabetes, is a term for several conditions involving how your body turns food into energy. when you eat a carbohydrate, your body turns it into a sugar called. Anyone with a body mass index higher than 25 (23 for asian-americans), regardless of age, who has additional risk factors, such as high blood pressure, abnormal cholesterol levels, a sedentary lifestyle, a history of polycystic ovary syndrome or heart disease, and having a close relative with diabetes. anyone older than age 45 is advised to receive an initial blood sugar screening, and then. Suggested articles video: caring for your diabetic cat obesity care of obese cats the special needs of the senior cat hyperthyroidism vomiting diabetes mellitus is a condition in which the body cannot properly produce or respond to the hormone insulin. this results in elevated levels of the sugar glucose, which is the main source of energy for the body. like the human body, the cells in a cat. Diabetes is diagnosed through blood tests that detect the level of glucose in the blood. fasting plasma glucose (fpg) test. a blood sample is taken in the morning after you fast overnight. a normal fasting blood sugar level is between 70 and 100 milligrams per deciliter (mg/dl).
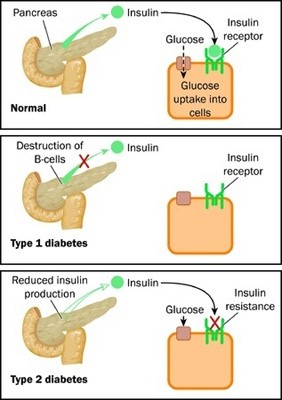
A diagnosis of diabetes mellitus is based on persistent fasting hyperglycemia and glycosuria. the normal fasting value for blood glucose in dogs and cats is 75–120 mg/dl. in cats, stress-induced hyperglycemia is a frequent problem, and multiple blood and urine samples may be required to confirm the diagnosis. In type 2 diabetes (adult onset diabetes), the pancreas makes insulin, but it either doesn't produce enough, or the insulin doesn't work properly. nine out of 10 people with diabetes have type 2. this type occurs most often in people who are over 40 years old but can occur even in childhood if there are diabetes melitus normal risk factors present.

What Is Diabetes Cdc
Diabetes mellitus: types, risk factors, symptoms, treatments.

Diabetesmelitus, dm (bahasa yunani: διαβαίνειν, diabaínein, tembus atau pancuran air) (bahasa latin: mellitus, rasa manis) yang juga dikenal di indonesia dengan istilah penyakit kencing manis adalah sekelompok gangguan metabolisme yang ditandai dengan kadar gula darah yang tinggi selama periode waktu yang lama. gejala umum yaitu sering buang air kecil, haus meningkat, dan nafsu. More diabetes mellitus normal images. Diabetesmellitus is the second most common endocrine disease in cats. it is seen more frequently in middle-aged to senior cats and is more common in males than females. while the exact incidence is unknown, the number of diabetic cats is increasing at an alarming rate due to the tremendous increase in the number of overweight and obese cats. The normal ranges for blood sugar levels in adults who do not have diabetes before eating or fasting the range begins at 72-99mg/dl while fasting ranges for those being treated for type 1 or type 2 diabetes range from 80 -130 mg/dl. according to the american diabetes association normal blood sugar levels before and after eating should be 80-130 mg/dl before eating a meal (fasting), and less.
Diabetesmellitus is a syndrome with disordered metabolism and inappropriate hyperglycemia due to either a deficiency of insulin secretion or to a combination of insulin resistance and inadequate insulin secretion to compensate. type 1 diabetes diabetes melitus normal is due to pancreatic islet b cell destruction predominantly by an autoimmune process, and these. Normal blood sugar levels for adults with diabetes normally, your pancreas releases insulin when your blood sugar or “ blood glucose,” gets high -after a meal, for example.
Comments
Post a Comment