Diabetes Complications Wikipedia
Aims: the diabetes complications severity index (dcsi) converts diagnostic codes and laboratory results into a 14-level metric quantifying the long-term effects of diabetes on seven body systems. adoption of the international classification of diseases, tenth revision, clinical modification (icd-10-cm) necessitates translation from icd-9-cm and. The term diabetes includes several different metabolic disorders that all, if left untreated, result in abnormally high concentration of a sugar called glucose in the blood. diabetes mellitus type 1 results when the pancreas no longer produces significant amounts of the hormone insulin, usually owing to the autoimmune destruction of the insulin-producing beta cells of the pancreas.
Type 1 diabetes simple english wikipedia, the free.
Diabetes mellitus type 1, also called type 1 diabetes, is an autoimmune disease that results in high blood sugar. this is because the body cannot create enough of the hormone insulin. people with this condition are insulin dependent they require insulin injections without which they may die. people with type 1 diabetes are at increased risk of stroke, heart disease or gangrene. Long-term complications of diabetes complications wikipedia diabetes develop gradually. the longer you have diabetes — and the less controlled your blood sugar — the higher the risk of complications. eventually, diabetes complications may be disabling or even life-threatening. possible complications include: cardiovascular disease. Type 2 diabetes is typically a chronic disease associated with a ten-year-shorter life expectancy. this is partly due to a number of complications with which it is associated, including: two to four times the risk of cardiovascular disease, including ischemic heart disease and stroke; a 20-fold increase in lower limb amputations, and increased rates of hospitalizations.
Complications Of Diabetes Wikipedia Republished Wiki 2
Gestational diabetes is a condition in which a woman without diabetes develops high blood sugar levels during pregnancy. gestational diabetes generally results in few symptoms; however, it does increase the risk of pre-eclampsia, depression, and requiring a caesarean section. babies born to mothers with poorly treated gestational diabetes are at increased risk of being too large, having low. Babies of mothers who have gestational diabetes have a higher risk of developing obesity and type 2 diabetes later in life. stillbirth. untreated gestational diabetes can result in a baby's death either before or shortly after birth. complications that may affect you. gestational diabetes may also increase your risk of:. Targets vary with the type of diabetes, age, and presence of complications. if you have gestational diabetes, your blood sugar targets will be lower than people with other types of diabetes.
Diabetes.
Diabetes Management Wikipedia
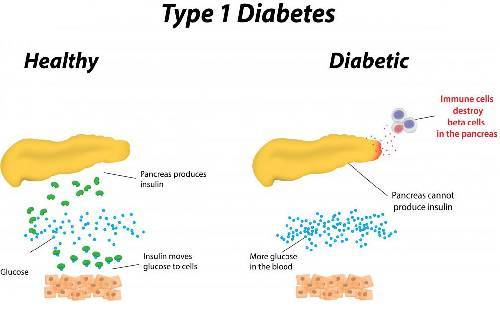
Cardiovascular disease: affects the heart and blood vessels and may cause fatal complications such as coronary artery disease (leading to heart attack) and diabetes complications wikipedia stroke. cardiovascular disease is the most common cause of death in people with diabetes. high blood pressure, high cholesterol, high blood glucose and other risk factors contribute to increasing the risk of cardiovascular complications. Type 1 diabetes (t1d), previously known as juvenile diabetes, is a form of diabetes in which very little or no insulin is produced by the pancreas. insulin is a hormone required for the body to use blood sugar. before treatment this results in high blood sugar levels in the body. the classic symptoms are frequent urination, increased thirst, increased hunger, and weight loss.
Diabetes mellitus (dm), commonly known as diabetes, is a group of metabolic disorders characterized by a high blood sugar level over a prolonged period of time. symptoms often include frequent urination, increased thirst, and increased appetite. if left untreated, diabetes can cause many complications. acute complications can include diabetic ketoacidosis, hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state, or. Type 2 diabetes can increase your risk of a number of complications that affect the feet. most diabetes-related foot issues are caused by nerve damage, sometimes referred to as neuropathy. Diabetes mellitus (dm), commonly known as diabetes, is a group of metabolic disorders characterized by a high blood sugar level over a prolonged period of time. symptoms often include frequent urination, increased thirst, and increased appetite. if left untreated, diabetes can cause many complications. acute complications can include diabetic ketoacidosis, hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state, or.
Diabetes is diabetes complications wikipedia the leading cause of new vision loss among adults ages 20 to 74 in the u. s. it can lead to eye problems, some of which can cause blindness if not treated: glaucoma. The complications of diabetes mellitus are far less common and less severe in people who have well-controlled blood sugar levels. acute complications include hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia, diabetic coma and nonketotic hyperosmolar coma. chronic complications occur due to a mix of microangiopathy, macrovascular disease and immune dysfunction in the form of autoimmune disease or poor immune. Ideal sources for wikipedia's health content are defined in the guideline wikipedia:identifying reliable sources (medicine) and are typically review articles. here are links to possibly useful sources of information about complications of diabetes.. pubmed provides review articles from the past five years (limit to free review articles); the trip database provides clinical publications about.
Complications of diabetes mellitus include problems that develop rapidly (acute) or over time (chronic) and may affect many organ systems. the complications of diabetes can dramatically impair quality of life and cause long-lasting disability. overall, complications are far less common and less severe in people with well-controlled blood sugar levels. Diabetes is a condition that results from lack of the hormone insulin in a person's blood, or when the body has a problem using the insulin it produces (insulin resistance). there is another disease with a similar name, diabetes insipidus, however they are not related. when people say "diabetes", they usually mean diabetes mellitus. people with diabetes mellitus are called "diabetics". The complications of diabetes mellitus are far less common and less severe in people who have well-controlled blood sugar levels. acute complications include hypoglycemia, hyperglycemia, diabetic coma, and nonketotic hyperosmolar coma. chronic complications occur due to a mix of microangiopathy, macrovascular disease and immune dysfunction in the form of autoimmune disease or poor immune. Complications of hypertension are clinical outcomes that result from persistent elevation of blood pressure. hypertension is a risk factor for all clinical manifestations of atherosclerosis since it is a risk factor for atherosclerosis itself. it is an independent predisposing factor for heart failure, coronary artery disease, stroke, kidney disease, and peripheral arterial disease.
Diabetes care: 10 ways to avoid diabetes complications (mayo foundation for medical education and research) also in spanish; diabetes, gum disease, and other dental problems (national institute of diabetes and digestive and kidney diseases) also in spanish; understanding blood sugar and control (american diabetes association); weight loss (american diabetes association). Skin complications. stay alert for symptoms of skin infections and other skin disorders common in people with diabetes. read more. eye complications. keep your risk of glaucoma, cataracts and other eye problems low with regular checkups. read more. neuropathy. nerve damage from diabetes is called diabetic neuropathy (new-rop-uh-thee). Type 2 diabetes is a result of both genetics and lifestyle. people who have relatives with diabetes type 2 are at an increased risk. they may develop diabetes if they have other risk factors in their lifestyle, for example obesity or low amount of exercise. complications.
Comments
Post a Comment